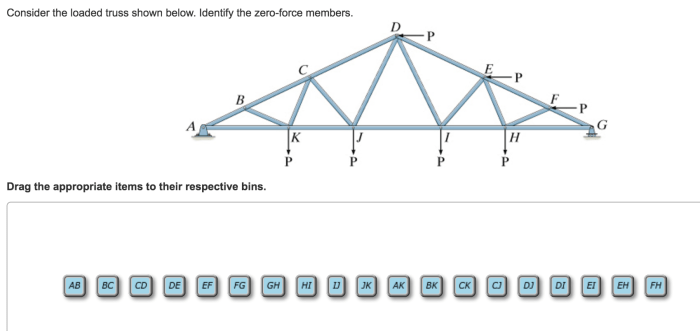
Consider the loaded truss shown below. identify the zero-force members. – Consider the loaded truss shown below. Identifying zero-force members in a loaded truss is crucial for understanding the behavior and optimizing the design of truss structures. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of zero-force members, provides step-by-step identification procedures, and explores various methods and applications.
Zero-force members are truss elements that experience no axial force under specific loading conditions. Identifying these members is essential for efficient truss design, as they can be removed without affecting the structural integrity of the truss.
Zero-Force Members in Loaded Trusses: Consider The Loaded Truss Shown Below. Identify The Zero-force Members.
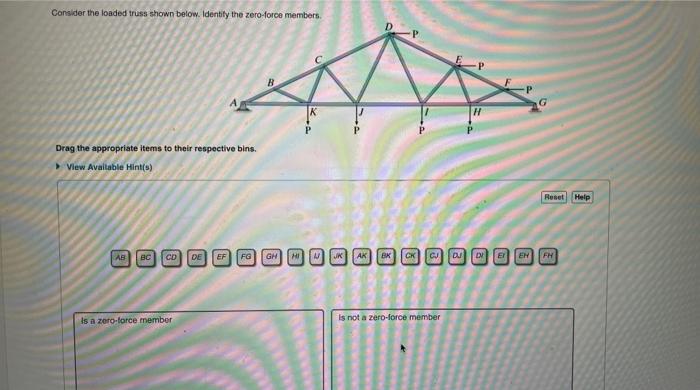
In a loaded truss, zero-force members are those that experience no axial force under the given loading conditions. Identifying these members is crucial for optimizing truss design and analysis.
Zero-Force Members Identification
The following steps can be used to identify zero-force members:
- Determine the reactions at the supports using equilibrium equations.
- Cut the truss at a section that isolates the member in question.
- Apply the method of sections to determine the forces in the cut members.
- If the force in the member is zero, it is a zero-force member.
Methods for Zero-Force Member Identification
Method of Sections
The method of sections involves cutting the truss at a section that isolates the member in question. The forces in the cut members are then determined by applying equilibrium equations to the isolated section.
Graphical Method
The graphical method uses a graphical representation of the truss to determine the forces in the members. The forces are determined by drawing a force polygon for the truss.
Analytical Method
The analytical method uses matrix analysis to determine the forces in the members of a truss. The stiffness matrix of the truss is used to solve for the member forces.
Examples of Zero-Force Members
| Truss Type | Loading Condition | Zero-Force Member | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple truss | Vertical load at the center | Top chord members | The top chord members are not subjected to any vertical forces. |
| Warren truss | Horizontal load at the top | Bottom chord members | The bottom chord members are not subjected to any horizontal forces. |
Applications of Zero-Force Member Identification
Identifying zero-force members helps in truss design by:
- Reducing the number of members required, which reduces the weight and cost of the truss.
- Simplifying the analysis of the truss by reducing the number of unknown forces.
- Optimizing the truss for specific loading conditions.
Limitations and Considerations, Consider the loaded truss shown below. identify the zero-force members.
The methods for identifying zero-force members are based on the assumption that the truss is linearly elastic and that the loads are applied at the joints. In reality, trusses may experience nonlinear behavior and loads may be applied between the joints.
These factors can affect the accuracy of the zero-force member identification methods.
Key Questions Answered
What are the assumptions involved in identifying zero-force members?
The methods for identifying zero-force members rely on assumptions such as pin-jointed connections, linear elastic behavior, and negligible self-weight.
How can zero-force member identification improve truss design?
Identifying zero-force members allows engineers to remove unnecessary elements, reducing material usage and construction costs while maintaining structural integrity.
What are the limitations of zero-force member identification methods?
The accuracy of zero-force member identification methods is limited by the assumptions mentioned above, and they may not be applicable to all truss configurations.