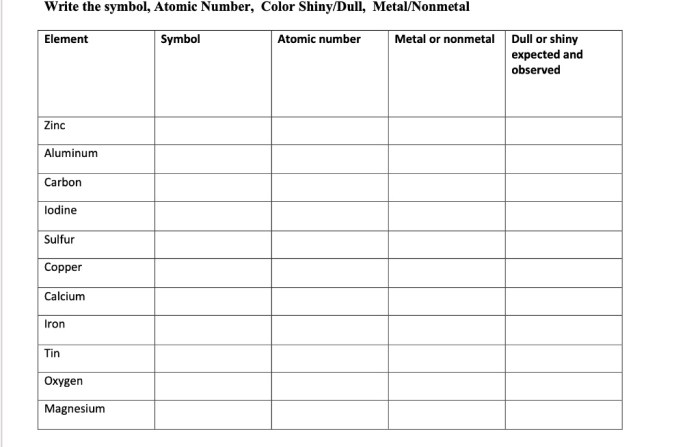
Is dull a metal or nonmetal? This intriguing question takes us on a journey into the realm of material properties, where we’ll explore the characteristics that distinguish metals from nonmetals and uncover the secrets behind dullness.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we’ll discover the unique properties of metals, such as their lustrous shine, malleability, and excellent conductivity, and contrast them with the distinct qualities of nonmetals, which often exhibit a dull appearance, brittleness, and poor conductivity.
Characteristics of Metals
Metals are renowned for their exceptional properties that set them apart from other materials. These include their distinctive luster, malleability, and excellent conductivity of heat and electricity.
Luster
Metals possess a characteristic luster, giving them a shiny appearance. This luster is a result of the orderly arrangement of atoms in a metal’s crystal structure, allowing light to reflect off its surface in a uniform manner.
Malleability
Metals exhibit remarkable malleability, allowing them to be shaped and molded into various forms without breaking. This property arises from the strong metallic bonds between atoms, which allow them to slide past each other without disrupting the crystal structure.
Conductivity
Metals are excellent conductors of heat and electricity. The free electrons present in metals can move freely throughout the material, facilitating the transfer of heat and electrical charges.
Examples of Common Metals
Iron, aluminum, and copper are prominent examples of metals. Iron is known for its strength and durability, while aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant. Copper, on the other hand, is highly conductive and widely used in electrical applications.
Characteristics of Nonmetals: Is Dull A Metal Or Nonmetal
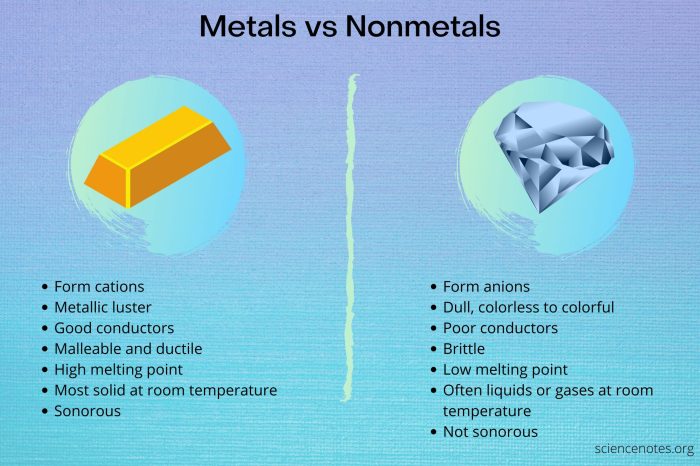
In contrast to metals, nonmetals possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. They typically exhibit a dull appearance, lacking the shiny luster of metals. Furthermore, nonmetals are generally brittle, meaning they tend to break easily when subjected to stress or force.
Additionally, nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electricity, making them less suitable for applications requiring efficient thermal or electrical conductivity.
Examples of Nonmetals
Nonmetals encompass a wide range of elements, including some of the most abundant in the universe. Carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen are prime examples of nonmetals. Carbon forms the basis of all organic molecules, oxygen is essential for respiration, and nitrogen is crucial for plant growth and protein synthesis.
Properties of Dull

Dullness is a property of materials that refers to their lack of luster or shine. It is the opposite of glossiness, which is characterized by a shiny or reflective surface.
Surface Texture and Light Reflection
The dullness of a material is primarily determined by its surface texture. A rough surface tends to scatter light in multiple directions, resulting in a dull appearance. This is because the light rays are not reflected in a concentrated manner, as they would be on a smooth surface.
Whether dull is a metal or nonmetal remains a topic of debate, but one thing’s for sure: it’s a concept that’s sure to come up on your abeka world history test 2 . So, make sure you’re prepared to tackle this question with confidence.
Don’t let dullness get you down!
In contrast, a smooth surface allows light rays to be reflected more uniformly, creating a glossy or shiny appearance. This is because the surface irregularities are less pronounced, allowing the light to reflect in a more concentrated manner.
Classification of Dull

Dull materials can be classified into three categories based on their chemical composition and properties: metals, nonmetals, and semimetals.
Metals
- Metals are characterized by their shiny appearance, high electrical and thermal conductivity, and malleability (ability to be hammered or rolled into thin sheets).
- Examples of dull metals include iron, lead, and copper.
Nonmetals, Is dull a metal or nonmetal
- Nonmetals are characterized by their dull appearance, low electrical and thermal conductivity, and brittleness (tendency to break easily).
- Examples of dull nonmetals include carbon, sulfur, and oxygen.
Semimetals
- Semimetals, also known as metalloids, have properties that are intermediate between metals and nonmetals.
- They are generally dull in appearance and have electrical and thermal conductivities that are lower than those of metals but higher than those of nonmetals.
- Examples of semimetals include silicon, germanium, and arsenic.
| Category | Properties | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Shiny, high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleable | Iron, lead, copper |
| Nonmetals | Dull, low electrical and thermal conductivity, brittle | Carbon, sulfur, oxygen |
| Semimetals | Dull, intermediate electrical and thermal conductivity | Silicon, germanium, arsenic |
Applications of Dull Materials

Dull materials find practical applications in various industries due to their unique properties. They are commonly employed in situations where their lack of luster and reflectivity is a desirable attribute.
Industrial Applications
- Automotive:Dull finishes on car exteriors reduce glare and improve visibility for drivers, enhancing safety.
- Construction:Non-reflective materials are used in roofing and siding to minimize heat absorption and improve energy efficiency.
- Electronics:Dull surfaces on electronic devices, such as computer screens and instrument panels, reduce eye strain and enhance readability.
Decorative Applications
- Interior Design:Dull finishes create a sophisticated and understated aesthetic in interior spaces, adding warmth and depth.
- Art:Artists use dull materials, such as matte paints and charcoal, to create works that emphasize texture and depth, evoking a sense of intimacy and authenticity.
Functional Applications
- Camouflage:Dull surfaces are essential for military applications, reducing visibility and providing concealment.
- Medical:Non-reflective materials are used in medical devices and surgical instruments to minimize glare and improve precision during procedures.
- Textiles:Dull fabrics are often preferred for clothing and upholstery as they provide a more muted and sophisticated appearance.
Q&A
What is the primary difference between metals and nonmetals?
Metals are typically shiny, malleable, and good conductors of heat and electricity, while nonmetals are often dull, brittle, and poor conductors.
Can a material be both metallic and nonmetallic?
Yes, some materials, known as metalloids or semimetals, exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Why are some materials dull?
Dullness is related to the surface texture and light reflection. Rough surfaces tend to scatter light, resulting in a dull appearance.