Polynomial functions and rates of change quiz – Embark on a journey through the realm of polynomial functions and rates of change with our engaging quiz. This comprehensive assessment will test your understanding of these fundamental concepts and their real-world applications. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of polynomial behavior and the secrets of calculating rates of change.
As we delve deeper into this mathematical exploration, we will encounter the varying degrees of polynomial functions, uncover their end behavior patterns, and harness the power of the power rule to determine rates of change. Along the way, we will uncover the practical significance of polynomial functions in diverse fields, from science to economics.
Polynomial Functions
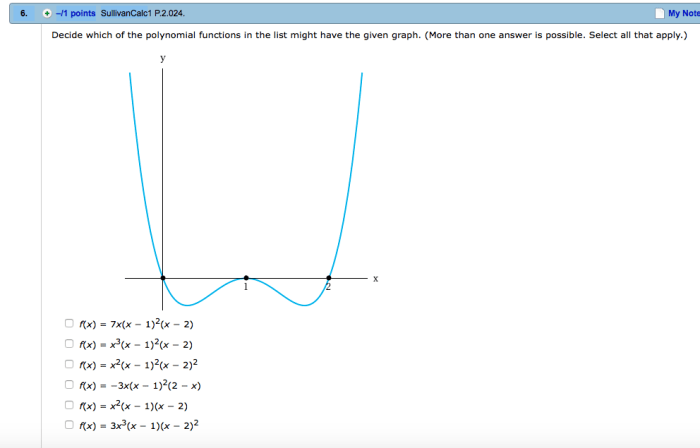
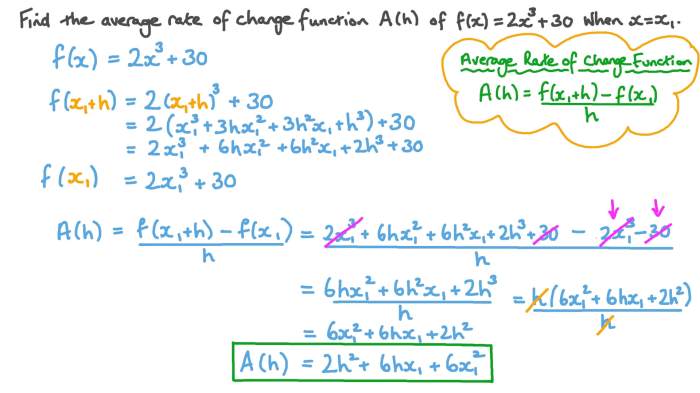
Polynomial functions are mathematical expressions that represent the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. They are characterized by terms that are powers of the independent variable.
The degree of a polynomial function is the highest exponent of the independent variable in the expression. Polynomial functions with different degrees exhibit distinct end behaviors as the independent variable approaches infinity or negative infinity.
Degrees of Polynomial Functions
- Linear function: Degree 1
- Quadratic function: Degree 2
- Cubic function: Degree 3
- Quartic function: Degree 4
- And so on
End Behavior of Polynomial Functions
The end behavior of a polynomial function depends on the degree and the leading coefficient (the coefficient of the term with the highest degree):
- Odd degree, positive leading coefficient: Rises to infinity on both ends
- Odd degree, negative leading coefficient: Falls to negative infinity on both ends
- Even degree, positive leading coefficient: Rises to infinity as x approaches infinity and falls to infinity as x approaches negative infinity
- Even degree, negative leading coefficient: Falls to negative infinity as x approaches infinity and rises to infinity as x approaches negative infinity
Rates of Change
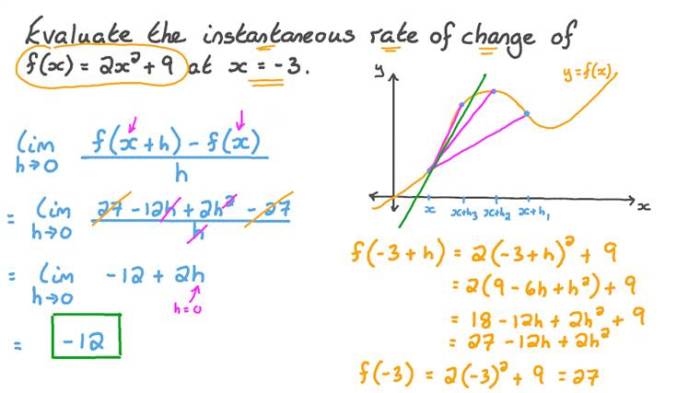
The rate of change of a polynomial function measures the instantaneous rate at which the dependent variable changes with respect to the independent variable.
Calculating Rates of Change
The rate of change of a polynomial function f(x) with respect to x is given by the power rule:
f'(x) = nx^(n-1)
where n is the degree of the polynomial function.
Examples of Rates of Change
- For f(x) = x^2, f'(x) = 2x
- For f(x) = x^3 – 2x, f'(x) = 3x^2 – 2
- For f(x) = 5x^4 + 3x^2 – 1, f'(x) = 20x^3 + 6x
Applications of Polynomial Functions: Polynomial Functions And Rates Of Change Quiz

Polynomial functions have numerous real-world applications in various fields:
Science, Polynomial functions and rates of change quiz
- Modeling projectile motion
- Fitting data to curves
- Approximating complex functions
Engineering
- Designing bridges and structures
- Analyzing fluid flow
- Optimizing manufacturing processes
Economics
- Modeling demand and supply
- Forecasting economic growth
- Optimizing investment portfolios
Questions Often Asked
What is the degree of a polynomial function?
The degree of a polynomial function is the highest exponent of the variable in the function.
How do you calculate the rate of change of a polynomial function?
You can calculate the rate of change of a polynomial function using the power rule, which states that the derivative of x^n is nx^(n-1).
What are some real-world applications of polynomial functions?
Polynomial functions have numerous real-world applications, such as modeling population growth, projectile motion, and the design of bridges and buildings.