The dense regular connective tissue microscope unveils the intricate architecture of this ubiquitous tissue, revealing its remarkable strength and resilience. This specialized microscope illuminates the arrangement of collagen fibers, providing insights into their vital role in supporting and connecting various tissues throughout the body.
Composed primarily of densely packed collagen fibers aligned in parallel, dense regular connective tissue exhibits unique mechanical properties that enable it to withstand tensile forces. Its presence in tendons, ligaments, and fascia underscores its critical function in transmitting forces and maintaining structural integrity.
Definition and Structure of Dense Regular Connective Tissue
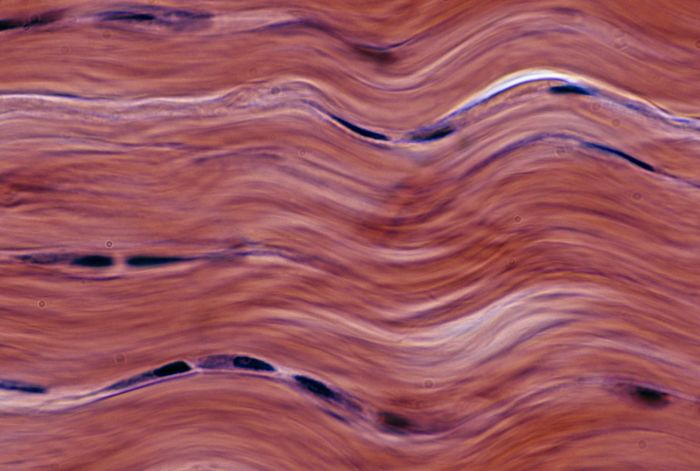
Dense regular connective tissue is a type of connective tissue characterized by its dense arrangement of collagen fibers. It provides strength, support, and flexibility to various tissues and organs in the body.
Composition and Arrangement
Dense regular connective tissue is composed primarily of collagen fibers, which are arranged in parallel bundles. These fibers are embedded in a ground substance consisting of proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and water.
Role of Collagen Fibers
Collagen fibers provide tensile strength and resistance to stretching. Their parallel alignment allows dense regular connective tissue to withstand forces applied in a specific direction.
Distribution
Dense regular connective tissue is found in various locations throughout the body, including tendons, ligaments, fascia, and the cornea of the eye.
Microscopic Appearance of Dense Regular Connective Tissue
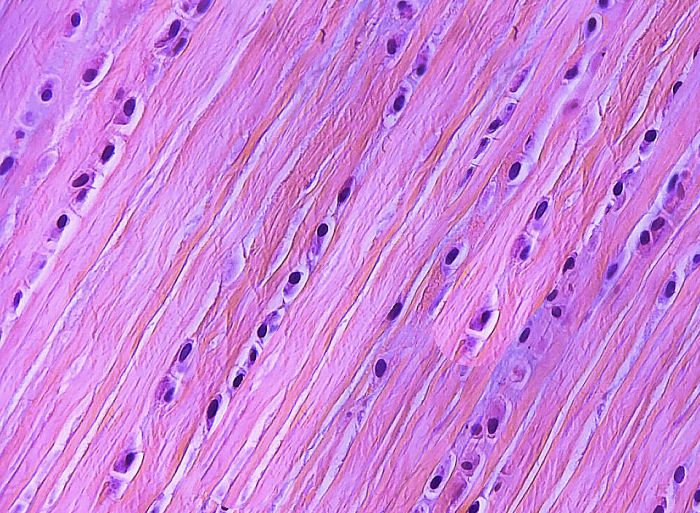
Under a microscope, dense regular connective tissue exhibits distinct characteristics:
Characteristic Features
- Parallel arrangement of collagen fibers
- Fibers are tightly packed, with minimal ground substance visible
- Nuclei of fibroblasts are flattened and elongated, oriented parallel to the fibers
Alignment of Collagen Fibers
The parallel alignment of collagen fibers gives dense regular connective tissue a striated or banded appearance under polarized light microscopy.
Images and Illustrations
[Ilustrasi mikroskopis dense regular connective tissue]
Functions of Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Dense regular connective tissue serves crucial functions in the body:
Mechanical Properties
- Provides tensile strength and resistance to stretching
- Supports and stabilizes tissues and organs
Force Transmission
Dense regular connective tissue transmits forces between different parts of the body, such as muscles and bones.
Tissue Integrity
It helps maintain the integrity of tissues by providing a structural framework and preventing excessive deformation.
Clinical Significance of Dense Regular Connective Tissue: Dense Regular Connective Tissue Microscope
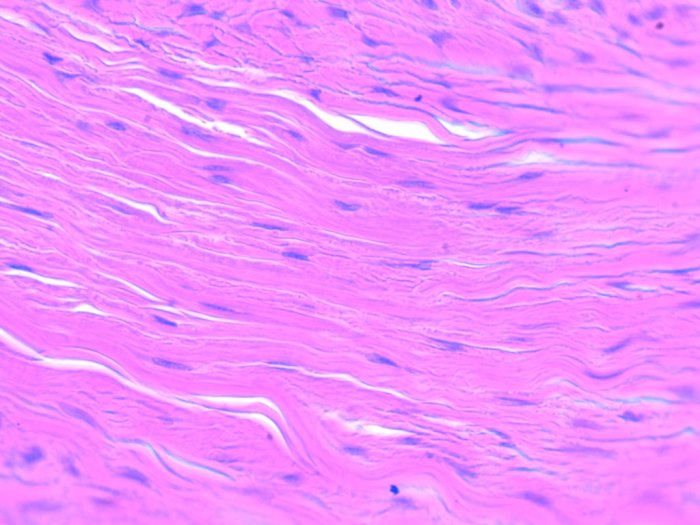
Dense regular connective tissue plays a vital role in health and disease:
Wound Healing and Tissue Repair, Dense regular connective tissue microscope
During wound healing, dense regular connective tissue forms scar tissue, which provides strength and support to the damaged area.
Abnormalities
Abnormalities in dense regular connective tissue can lead to conditions such as tendinitis, ligament sprains, and hernias.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications
- Microscopic examination of dense regular connective tissue can aid in the diagnosis of diseases.
- Tissue engineering techniques use dense regular connective tissue as a scaffold for regenerating damaged tissues.
FAQ Resource
What is the primary component of dense regular connective tissue?
Collagen fibers
Where is dense regular connective tissue commonly found in the body?
Tendons, ligaments, and fascia
What is the function of dense regular connective tissue?
To provide strength, support, and transmit forces